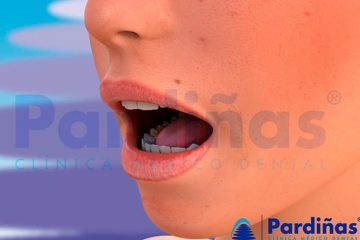
Canker sores are one of the most widespread oral health problems. Mouth ulcers are superficial lesions that appear in the soft tissues of the mouth such as lips and tongue. These can be painful and cause problems with speaking and eating. The types of sores vary in their severity and causes.
1) Why do canker sores appear?
The sores could be the symptom of a systemic illness such as a bacterial, viral or fungal infection or as a result of irritation caused by braces, dentures or the sharp edge of a broken tooth or filling. Depending on its origin, there are different types of canker sores:
1a. Traumatic sores or mouth ulcers:
They are wounds caused by trauma (bites, accidental hits, etc.), by the use of prostheses that are not well adapted, by friction with a broken tooth, by irritation caused by orthodontics, by burns, etc.

1b. Canker sores secondary to chemotherapy or radiotherapy:
It is a frequent side effect that occurs in patients under cancer treatment. Drugs such as Methotrexate, 5-Fluoracil, Doxorubicin... can cause this type of injury in the mouth. Head and neck radiotherapy can also cause mucositis and the appearance of ulcers on the mucosa and tongue.

1c. Recurrent aphthous stomatitis:
It is the most common form of sores in children, although they are also related to stress in young and adult patients. The exact cause is unknown, although it is thought to be multifactorial, such as predisposing genetic factors, alterations in the body's defenses, or related to systemic diseases (such as Crohn's syndrome, celiac disease, etc.).
Iron deficiencies or vitamins such as B1, B2 and B6 can influence the immune system, favoring the appearance of sores. Similarly, hormonal changes such as those present in the menstrual cycle are related to the appearance of canker sores.
Finally, quitting smoking can also lead to sores. In smoking patients, the thickness of the keratin layer that covers the mucous membranes is wider, which would be a protection against canker sores.
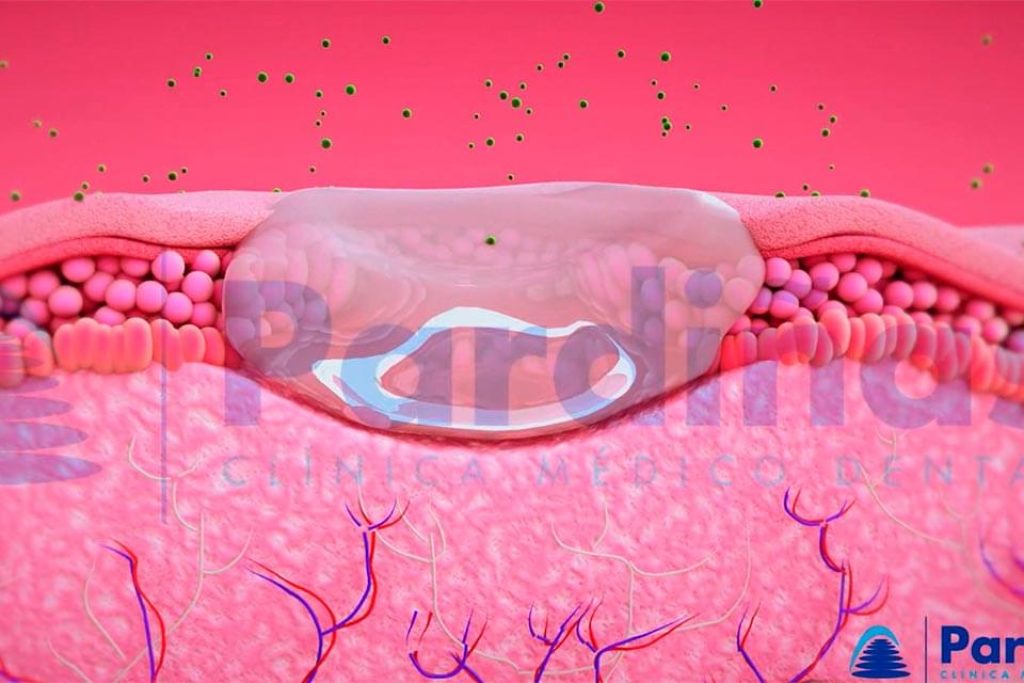
1d. Sores caused by infectious diseases:
The most common is the Herpes virus (HSV-1), which produces ulcers on the mucosa or lips, colloquially known as cold sores, and which are highly contagious.
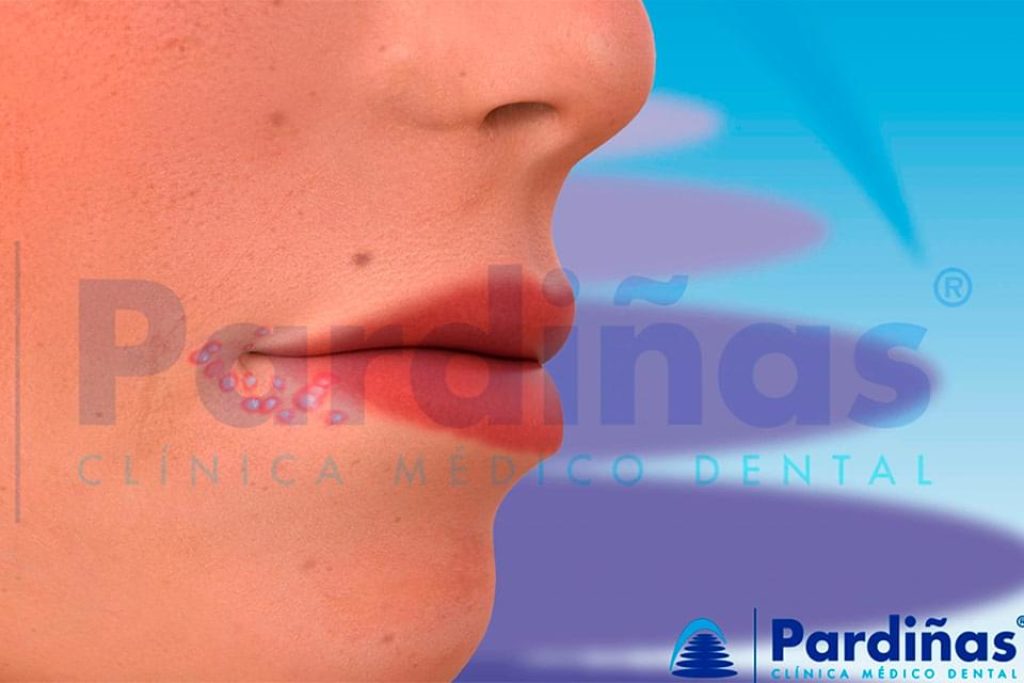
2) How to cure canker sores:
Smaller canker sores usually disappear without sequelae after 10-14 days, while larger ones can last up to a month and can leave a scar. Depending on their origin, the treatment may be different:
2a. Symptomatic treatment for mouth sores:
In general, the treatment of canker sores is usually symptomatic, applying protective gels, rinses with chlorhexidine or topical anesthetics, and most disappear on their own after a few days. In more serious cases, the dentist may prescribe the use of topical corticosteroids.
2b. Other recommendations for the treatment of mouth ulcers:
In any situation, it is important to maintain proper oral hygiene, to avoid an infection of this type of ulcer. It is also recommended to avoid eating spicy, acidic or irritating foods that can aggravate the condition of the ulcers, as well as the use of mouthwashes that contain alcohol or other irritating agents. Finally, it is necessary to evaluate the causes and check if there is any vitamin deficiency, allergy, infection or local trauma.

It is important to ask your dentist and examine any mouth ulcer that lasts 14 days or longer. In the same way, it is also recommended to review any lesion in the mouth that is present for more than 21 days. Could we help you?