Oral piercings are in fashion, but they are not harmless, they can cause numerous complications and injuries if they are not worn correctly. In this article we talk about piercings in the mouth and their possible risks.
What complications can oral piercings cause?
As we anticipated, the inappropriate use of oral piercings can trigger some complications in oral health:
Damage after the placement of the oral piercing
After the placement of an oral piercing, it is frequent to experience inflammation of the pierced area, pain, difficulty in speaking and chewing, bleeding, hypersialia (excessive production of saliva), infection and paresthesia (sensation of numbness of the lips or tongue). In addition to the typical damage after drilling, there are also injuries to the gums and hard and soft tissues, both extraoral and intraoral.

Hard tissue injuries from the use of oral piercings
Fissures are the most frequent damage, followed by abrasions and finally pigmentations. Fissures are produced by continuous trauma of the piercing metal with the surface of the tooth and can lead to its loss. Abrasions are produced by the continuous contact or friction of the metal of the piercing with the enamel of the tooth. Pigmentations are localized spots that usually occur in soft tissues. In the case of oral piercings, they can cause green or black pigmentation, due to the corrosion of metals.
The consequences of oral piercings in the soft tissues of the mouth
With regard to the soft tissues, the lesion that occurs most often is the imprint (mark on the tissues due to continuous pressure on them), gum recession, followed by depapillation, keloids and ulcers.
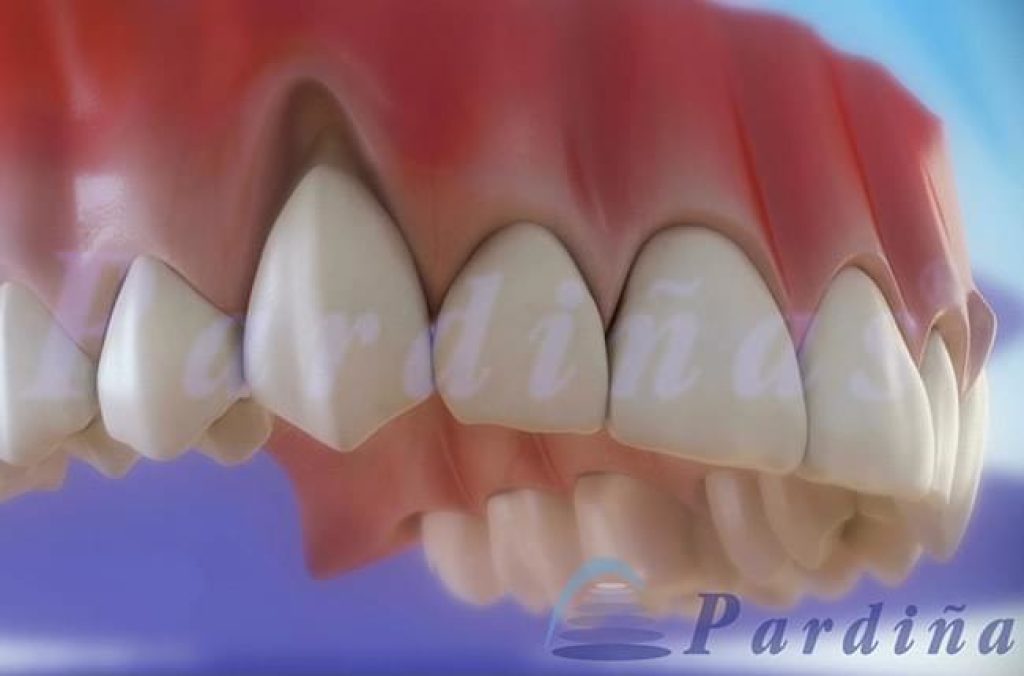
Damage to the gum from the use of oral piercings
If any injury worries dentists above the rest, it is the periodontal one, since it occurs in almost half of all piercing wearers. These increase in subjects with metal piercing and intraoral placement, especially in the case of gum piercings.These can first appear as lesions in the gum tissue, and later as a recession in the gums, which also leads to an aesthetic problem. It is important to understand that before the gums can retract, some of the underlying bone in the jaws must be lost. When the gums retract, the roots of the teeth are exposed, favoring the development of dental caries as the roots lack the protective enamel covering of the tooth's crown.

That's when the real problem begins, because as soon as the hard outer layer of your teeth is penetrated or cracked, your health is in jeopardy. If it continues to deepen, it can reach the pulp tissue, blood vessels and nerves. Once exposed, something as simple as air and saliva can begin to hurt, swell, and cause discomfort. But what usually happens is that those sensitive areas within the tooth can be attacked by toxic bacteria. Bacteria create an infection, and this leads to inflammation and the tremendous pain of having the nerve surrounded by diseased tissue.

Taste alterations due to the use of oral piercings
The use of these types of elements can cause dysgeusia, that is, alterations in taste, especially in cases of tongue piercings due to the damage that this causes to the nerves and blood vessels.

Bad breath
If oral hygiene is not extreme, the use of oral piercings can also cause bad breath problems due to the accumulation of food debris and plaque in the pierced area.

How to avoid the risks of using oral piercings
Although our clinic advises against the use of this type of piercings, it is possible to reduce their impact by taking into account a series of recommendations:
Avoid contact of the piercing with teeth and gums
Tongue piercings and the lip should be positioned and worn in such a way that they cannot collide with the teeth. It should never come into contact with the teeth or interfere with the bite. To ensure this, it is recommended to wear only small pieces of jewelry. Additionally, piercings should not be able to rotate on the inside of the lip, where it could come into contact with the teeth and gums and cause abrasive action, tearing or cutting of tissue, or chipping and cracking of tooth enamel.
Use good quality piercings
It is important to always use surgical grade stainless steel, titanium, 14 karat gold or other appropriate piercings to avoid problems related to lower quality metals.

Extreme oral hygiene
It is essential to maintain correct oral hygiene, making sure that the teeth and gums are clean, as well as the piercing materials.

Visiting the dentist frequently
Although it is always advisable to visit the dentist regularly, it is recommended to do it more frequently for those with piercings in the mouth, thus having greater control of their oral health. In this way it is possible to ensure that the piercing will not compromise your oral health. If you live in A Coruña and you are a carrier of piercings, our team of doctors will be happy to assist you.