At the time a baby is born, parents often ask themselves many questions about their newborns. In this post we want to answer the most common questions about baby teeth and children's oral health.
-
0) Pregnancy and oral health
- 1) What is teething?
- 2) Dental hygiene in babies and children
- 3) The definitive teeth
- 4) Most common oral diseases in childhood
-
5) The pediatric dentist can help you
0) Pregnancy and oral health
The oral health of a baby must begin with the care of the mother's oral health. It is easier for a child to have a healthy mouth if her mother has it. Therefore, it is essential to take extreme oral hygiene and visit the dentist more frequently during pregnancy.

1) What is teething?
Teething is the process by which an infant's first teeth come through a baby's gums. Tooth eruption is the process by which teeth work their way through the gums until they become visible in the mouth. The human being goes through this process on two occasions throughout life: the eruption of baby teeth and that of permanent teeth.
1A) When do baby teeth come in?
Milk teeth, or deciduous teeth, are those that appear during childhood and that are lost (generally) sequentially and being replaced by the permanent teeth. Deciduous teeth are divided into incisors, canines and molars, and there are a total of 20 teeth that normally erupt during the first two years of life.
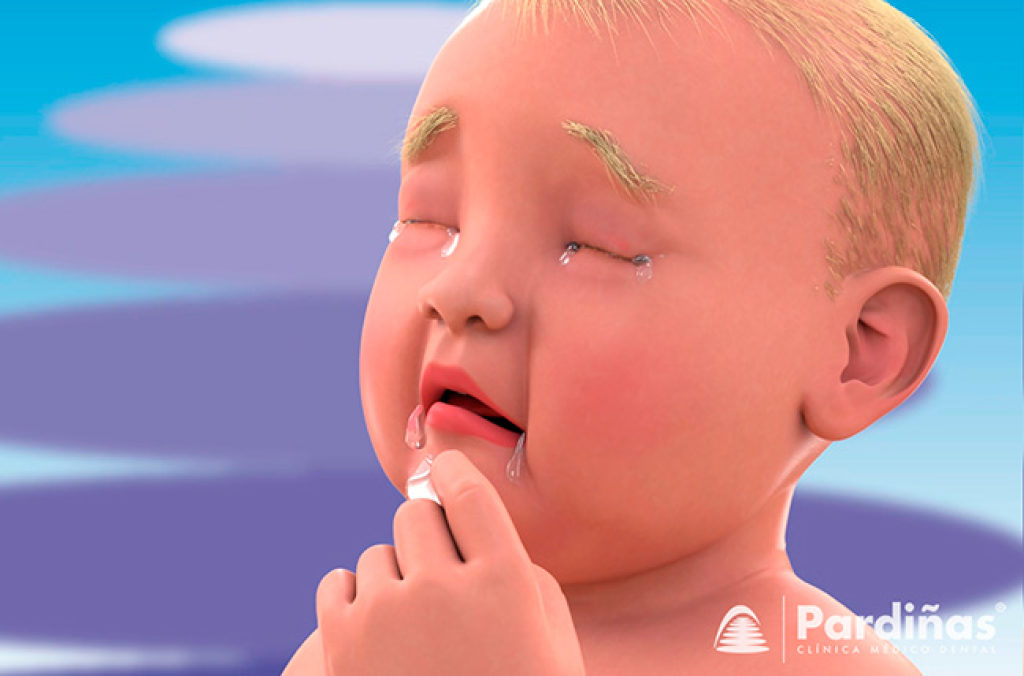
1Aa) What order do baby teeth come out?
The first teeth to appear are the lower central incisors between the sixth and eighth months. At nine months the upper central incisors begin to erupt, followed by the upper and lower lateral incisors after the first year. The first upper and lower milk molars emerge from the fifteenth month. Then it will be the canines around the eighteenth month. Finally, after 2 years, the second milk molars will come out.
1Ab) What symptoms does a baby have during teething?
When the first baby teeth begin to erupt, the baby may experience symptoms such as the urge to bite, excessive salivation, crying, irritability, and even a low-grade fever.

1Ac) What to do when a baby is teething?
The discomfort caused by the eruption of the first teeth can lead to a complex stage for parents. Local cold can be a great ally in this cause, so slightly chilling teethers, toys or even the feeding bottle in the refrigerator, can help alleviate these symptoms.

1B) Can the use of a pacifier affect the development of the mouth?
The use of a pacifier or prolonged sucking of the thumb beyond 3 years, can cause problems of dental malposition. There are specific devices to avoid these bad habits, which may also require the collaboration of a speech therapist.

1C) Can a baby be born with teeth?
Some babies are born with natal teeth. These can be fully formed, be supernumerary or have some anatomical defect; it is important to evaluate each case to see whether or not it is necessary to extract them. They are usually removed at the time of birth as a general rule, as they can lead to various problems such as falling and the baby choking. It also poses some difficulty when breastfeeding, as it can irritate or injure the mother's nipples.
1D) What happens if a baby's teeth don't erupt?
Each baby is different and, although there is a chronology of tooth eruption more or less common in humans, the times can vary significantly between children. If the process takes too long, it is advisable to consult professionals in case there are any abnormalities in the development.

2) Dental hygiene in babies and children
The care of the baby's mouth must be carried out from the lactation period with a series of appropriate measures after each milk intake. It is essential to maintain proper dental hygiene habits throughout childhood.
2A) When should you start washing a child's mouth?
Hygiene should start even before tooth eruption. At that time it is recommended to massage the baby's gums with a damp gauze or cloth. As soon as the baby's first tooth is born, it is recommended to include a little toothpaste (with 1000 parts per million fluoride) and wash them with a special gauze or thimble. There are also small brushes adapted to these cases.
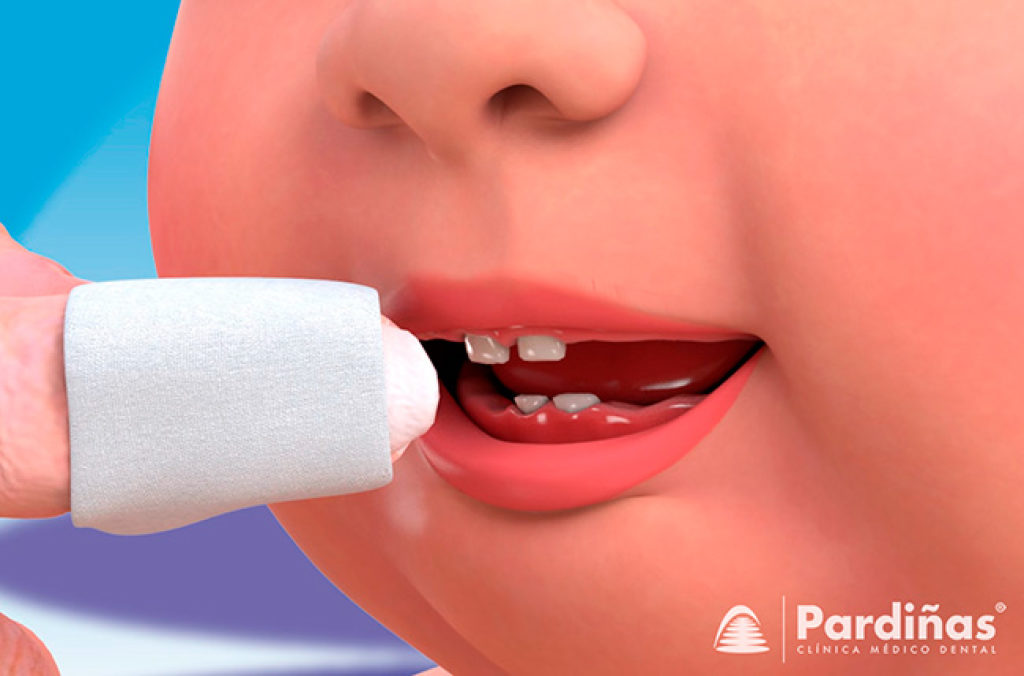
2B) How do you brush a baby's teeth?
It can be done with thimbles or brushes with very soft bristles and a smaller head to adapt to their mouths. It is important to teach your child the correct brushing techniques and make it a daily hygiene habit. At first it is recommended that the adult be present. Young children do not have a fully developed spitting reflex until they are 3 years old and can accidentally swallow toothpaste.

2C) How does a child have to brush their teeth?
It is essential that children who start brushing themselves do it right from the beginning. It is recommended to do it after each meal, starting with dental floss, and brushing for about three minutes with the proper technique, a medium-hard brush and little toothpaste, and rinsing thoroughly. It is important to brush the tongue as well. Until children are 7 or 8 years old, they usually do not have enough dexterity to do effective cleaning, so it is advisable to supervise them. In this video we show you one of the best ways to brush.
2D) What kind of toothpaste should they use?
If the child is between 6 months and 3 years old, it is recommended to use a toothpaste with 1000 parts per million (PPM) of fluoride in very little quantity: like a grain of rice. Between 3 and 5 years old the same type of toothpaste but in greater quantity: the size of a pea. From the age of 5, toothpastes with a minimum of 1450 PPM fluoride, but in the same amount, can be used.

2Da) Fluoride: a fundamental ally in the oral hygiene of the little ones
Fluoride is especially recommended during the tooth formation stage as it increases the hardness of the enamel and reduces the risk of cavities. The one contained in tap water is usually sufficient, although in some children it is advisable to reinforce the consumption of fluoride.
2E) Can cavities appear in baby teeth?
The enamel layer of milk teeth is thinner and more porous than permanent teeth, so kids are more prone to cavities if proper care is not followed. Even if these teeth fall out, any cavities or problems they develop in childhood can harm their permanent teeth.

2Ea) Feeding bottle tooth decay
Feeding bottle tooth decay is a typical problem in babies. It occurs because some parents put in the feeding bottle sucker sugar or honey, so that the baby falls asleep or calms down. If the little one is in contact with this sweet substance for a long time, these carbohydrates are ideal for the development of bacteria that cause tooth decay.

2Eb) How to avoid cavities in baby teeth
The use of dental sealants is an effective preventive treatment to protect against possible cavities. Sealing consists of demineralizing the enamel surface with a specific acid, and then covering it with a resin that hardens when polymerized with a special light.
3) The definitive teeth
The permanent dentition is the one that will replace and expand the deciduous one. These teeth are classified in the same way as those of the baby but there is an additional category called premolars, which are located between the canines and the molars. There are thirty-two permanent teeth, including the wisdom teeth.
3A) Why do baby teeth fall out?
Deciduous teeth fall out due to the push of permanent teeth. When the permanent dentition is already formed, it begins to emerge, gradually reabsorbing the roots of the milk teeth, which eventually fall out.
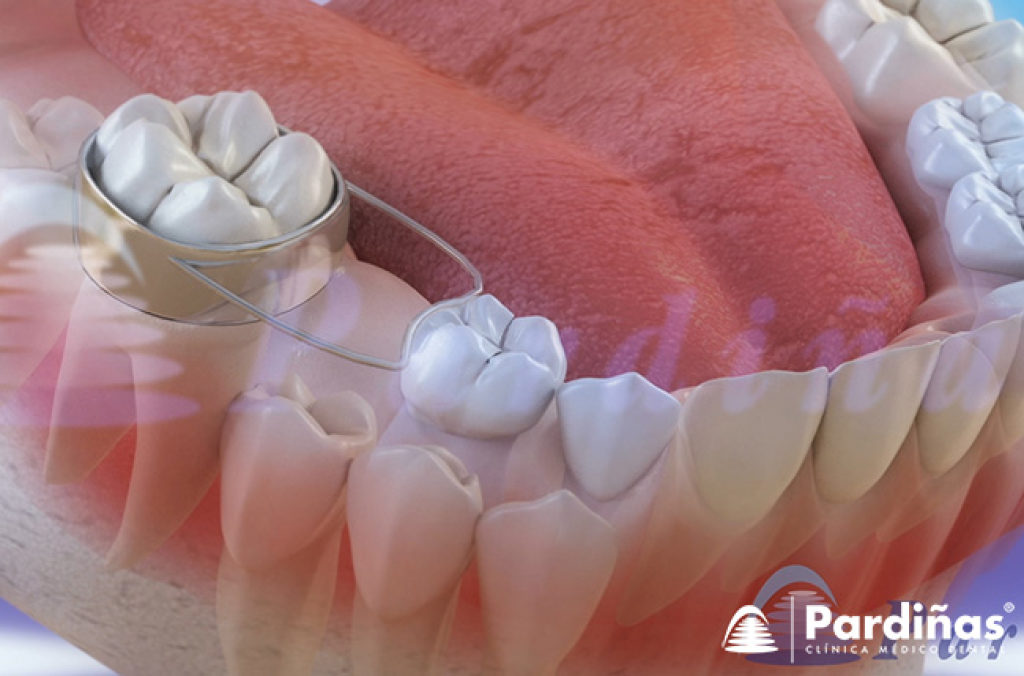
3Aa) What happens if baby teeth fall out prematurely?
When a deciduous tooth is lost prematurely, the adjacent teeth will tend to occupy the space left by the missing one, causing permanent impactions that prevent its normal eruption and generate malposition of the teeth. To avoid these problems, a space maintainer can be placed until the permanent tooth erupts, ensuring that it will have enough space to do so normally.
3Ab) What happens if baby teeth don't fall out?
In some cases baby teeth do not fall out. This may be due to something that hinders this process or to the non-existence of a definitive tooth. This second case is known as agenesis and its origin is genetic, so it is common for it to occur in different members of the same family. Ankylosis is another reason why deciduous teeth do not fall out, a disorder in which the baby tooth is attached to the bone. This can also be genetic or caused by trauma.
3B) What are impacted teeth?
Sometimes the fangs (canines) or other teeth can be retained within the bone and not erupt due to a lack of space, trauma, agenesis, etc. This problem is known as impacted tooth, and it can be solved with various techniques, including orthodontic traction. To do this, an access to the tooth is created through the gum and bone, and a button is attached to the tooth. The tooth is then tractioned little by little until it is placed in its correct position.
3C) When do the permanent teeth come out?
Definitive teeth begin to erupt around 6 - 7 years of age. The first teeth to erupt are the upper and lower first molars, followed by the lower central incisors. At 7 - 8 years, the upper centrals and the lower laterals emerge. At 8 - 9 years the upper lateral incisors come out. At 9 - 10 years the lower canines or fangs come out. At 10 - 11 years the upper premolars and the lower first premolars emerge. At 11 - 12 years, the upper canines and lower second premolars emerge. At 11 - 13 years the lower second molars come out. At 12 - 13 years the upper second molars come out.
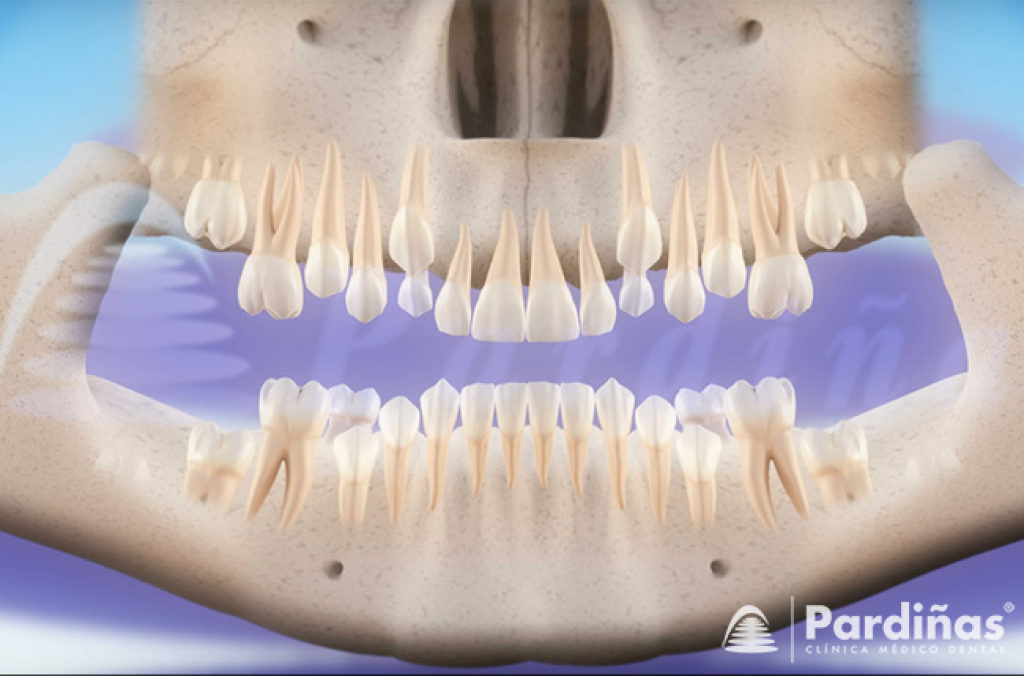
3D) When do wisdom teeth come out?
Wisdom teeth usually erupt between the ages of 17 and 24, but not everybody develops them or have them erupted. They are also known as wisdom teeth or third molars. These can come out without causing any discomfort, but in some cases they erupt in a malposition due, generally, to a lack of space in the jaw. In those situations it is necessary to remove them.
4) Most common oral diseases in childhood
The immune system of babies and children is not sufficiently developed, so childhood is a stage prone to the development of diseases, including oral ones. Most of them are not serious, but it is convenient to know some of the most frequent ones in order to be forewarned.
4A) Oral thrush in babies
Oral thrush is very common in newborns and infants younger than 6 months. It can occur due to contamination in childbirth if the mother suffers from vaginal yeast infection or from the act of breastfeeding.
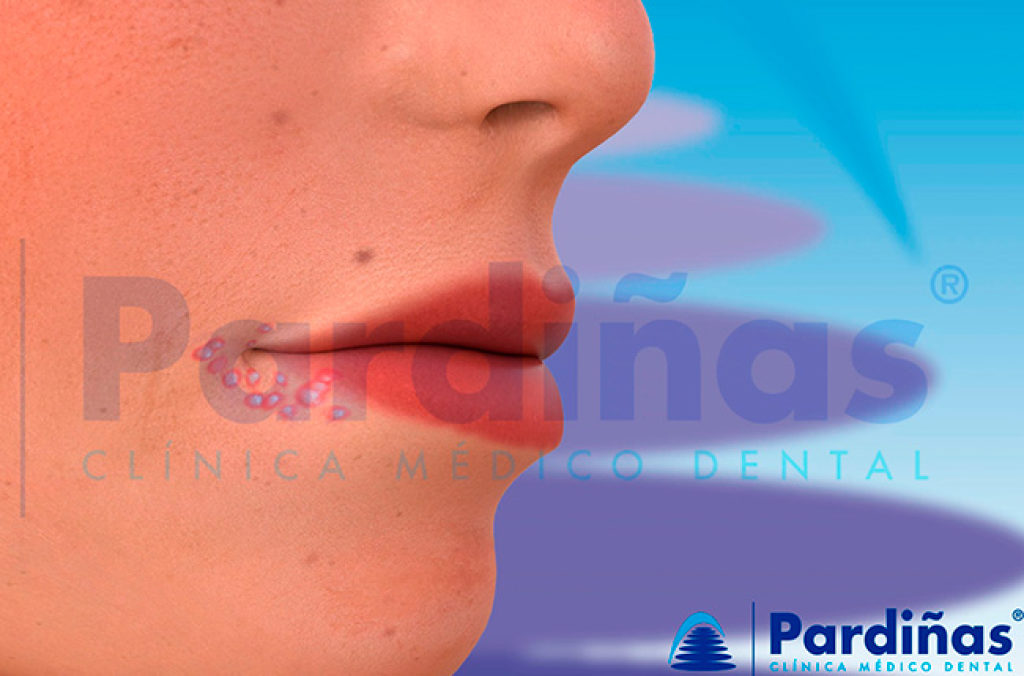
4B) Oral herpes in children
Childhood is also a time for the development of herpes. This first contact and infection with the herpes virus is usually asymptomatic, but it can also cause herpetic gingivostomatitis, which is the most common cause of stomatitis in children aged 1-3 years. This condition usually causes a high fever, malaise, headache, decreased appetite, and a sore throat. After a few days the gums become inflamed and cause great pain when swallowing. A couple of days later, multiple blisters appear anywhere in the mouth.

4C) Child bruxism
Bruxism (involuntary grinding or clenching of the teeth) is a common problem in children. It is a physiological bruxism, related to the stimulation and normal development of the mouth. This bruxism can occur in the deciduous teeth and disappear as the permanent teeth emerge. It can also be related to states of anxiety, nervousness or stress in childhood.

4D) Dental trauma
The blows are frequent in childhood and it is not strange that they can lead to the fissure, breakage or avulsion of a tooth. If the tooth has been knocked out, it must be taken without touching the root, DO NOT wash it and place it in a special device that allows it to be kept for up to 24 hours and urgently go to the dentist for its repositioning. If we do not have such a device, it can also be stored in milk for a few hours.

4E) Mononucleosis or kissing disease
Mononucleosis is an infection caused by the Epstein-Barr virus, which belongs to the herpesvirus family. Most infections take place in childhood and, especially, in adolescence. This is transmitted through oral secretions and can be spread through intimate contact. The virus has a long incubation period, 30 to 50 days, and symptoms include lesions in the oral cavity, pharyngitis, fever, poor appetite, fatigue, tiredness, swollen glands, etc. Treatment is usually symptomatic with anti-inflammatories or pain relievers to reduce fever, pain, and inflammation.
4F) Mumps
Mumps is a contagious disease caused by the Paramyxoviridae virus and located in the parotid glands. Although it can occur in adults, it is very common in childhood. Mumps can cause swollen salivary glands, pain when chewing or swallowing, fever, headaches, muscle aches, and even loss of appetite. There is no effective treatment for the disease beyond the use of Paracetamol/Acetaminophen to reduce fever and some symptoms. The best prevention is the MMR vaccine.
5) The pediatric dentist can help you
Pediatric dentists take care of children's oral problems. When the child reaches the first year of age, it is recommended to start going with him to the specialist at least once a year. If you live in A Coruña, our team of specialists will be happy to assist you.